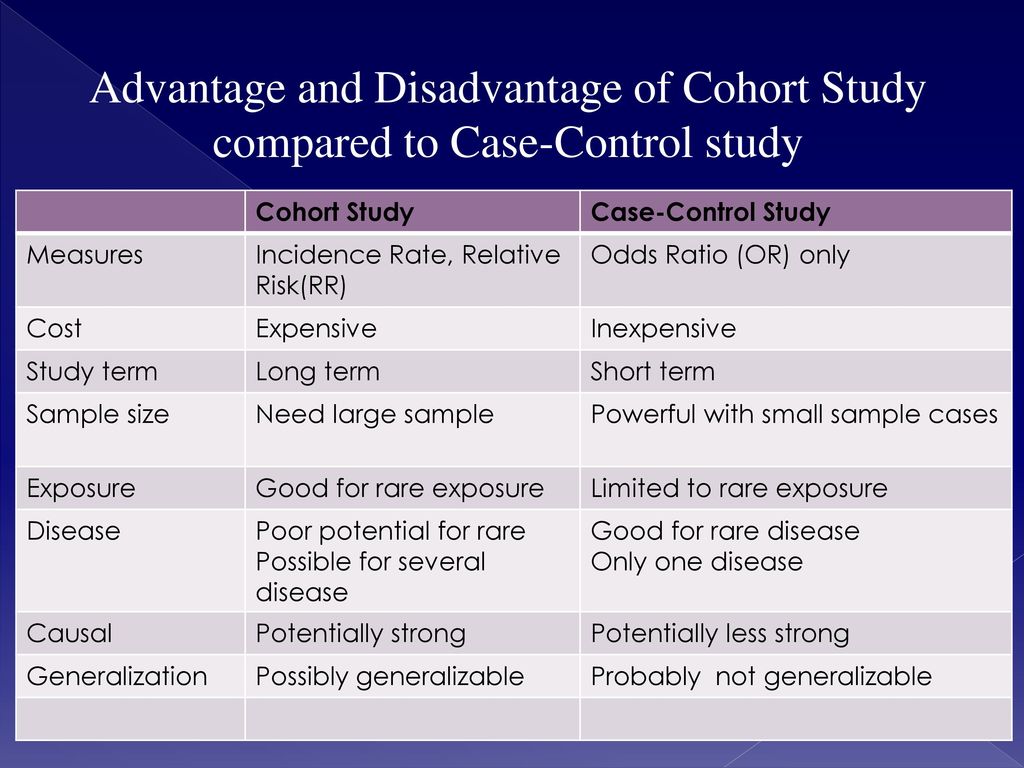
Davies et al (1) state that the odds ratio is a common measure in casecontrol studies, cohort studies, or clinical trails Unfortunately, this first sentence of their article is not correct For different study designs, OR should only be used as a measure of effect size when RR can not be estimated directly Other O does not have an R (cOhort), which means the other group does not have the risk factor Compare the two to see who gets the disease How to remember that case control studies measure odds ratio and cohort studies measure relative risk You take surgical "cases" to the "OR" (Operating room) Case control study Odds Ratio cohoRRRRRRt 2) Cohort studies will have information about persontime at risk, and so the desired outcomes are often incidence rates, population attributable risk, or risk ratios The odds ratio estimate for rare outcomes will approximately estimate the risk ratio in this design, but it makes more sense to compute the risk ratio directly
Effect Sizes Basicmedical Key
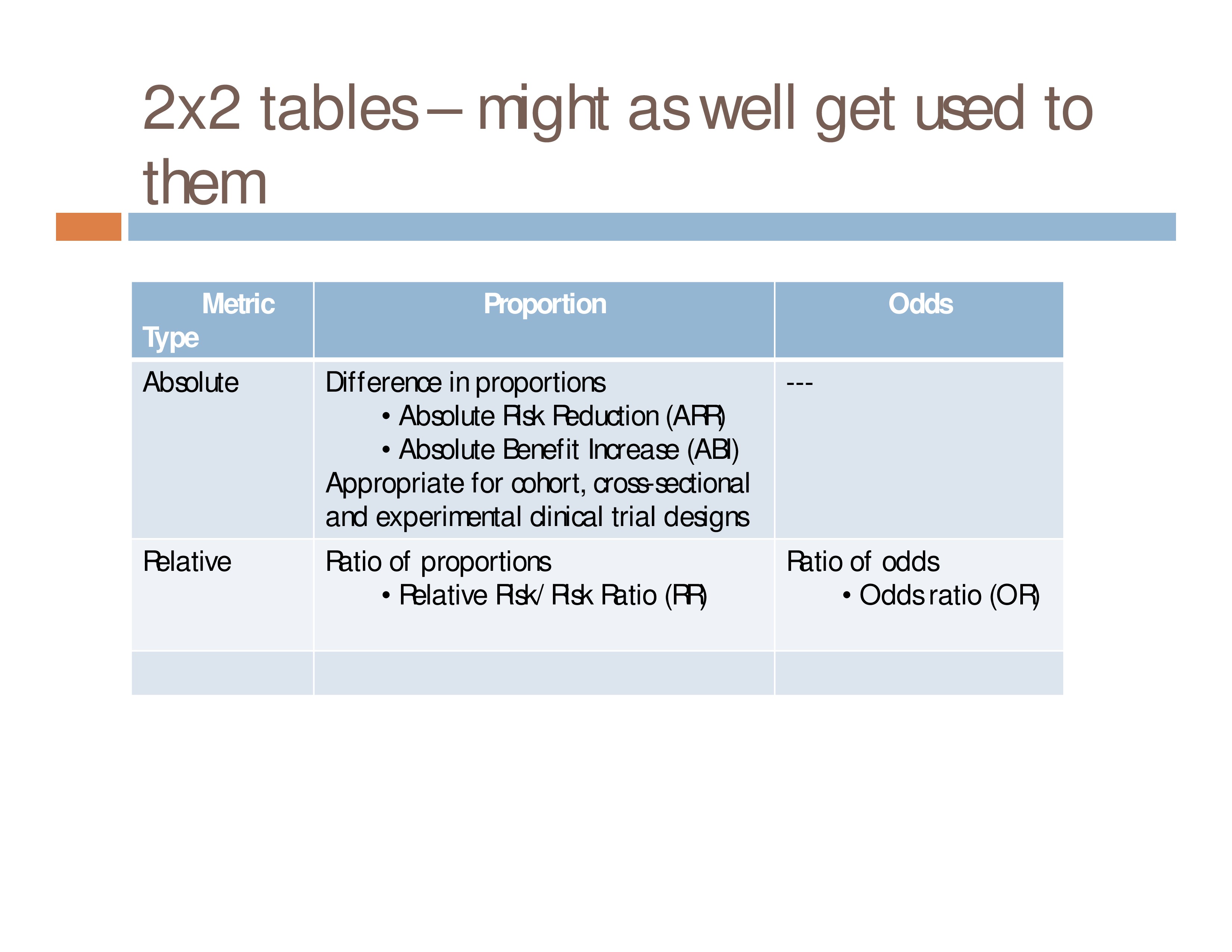
Odds ratio vs relative risk cohort
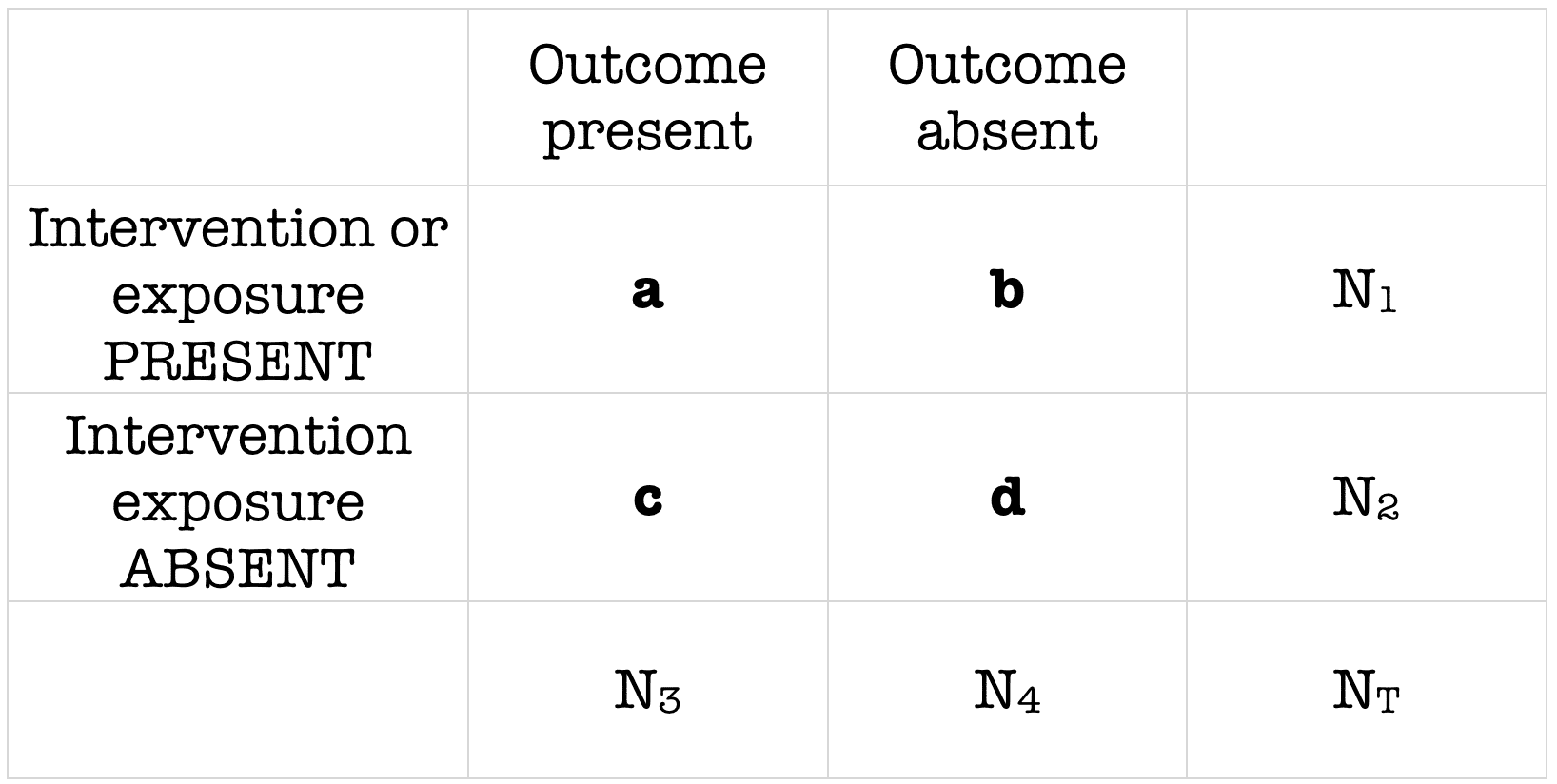
Odds ratio vs relative risk cohort-In epidemiological terms, the odds ratio is used as a point estimate of the relative risk in retrospective studies Odds ratio is the key statistic for most casecontrol studies In prospective studies, Attributable risk or risk difference is used to quantify risk in the exposed group that is attributable to the exposure In retrospective studies, attributable risk can not be calculated The odds ratio (OR) is the ratio of the odds of cancer in smokers to the odds of cancer in nonsmokers OR = (a/b)/ (c/d) = (ad)/ (bc) The risk ratio (RR), also called the relative risk, is the ratio of the probability of cancer in smokers to the probability of cancer in nonsmokers Given that you know a, b, c, and d, you can compute either of




Society For Birth Defects Research And Prevention
I won't write here the equation for the Odds Ratio in a cohort study, because it would be exactly the same as the population odds ratio, therefore they are also the same Therefore, the odds ratio is an effect size measure that is adequate for both casecontrol and cohort designs, because they all measure the same thing The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (The relative risk is also called the risk ratio) Let's look at an example Relative Risk/Risk Ratio Suppose you have a school that wants to test out a new tutoring programความเสี่ยงสมพันธั์ (Relative risk) risk ratio relative risk เท่ากับ ค่าอัตราส่วนของ p1/p2 Cohort Study risk ratio = 12/22 =55;
ERRATA At about the 300 mark the slide says "10,00" when it is really supposed to say "10,000" I added a pop up box to fix it Thanks to Mehdi Hedjazi forWhen the disease is rare, the odds ratio will be a very good approximation of the relative risk The more common the disease, the larger is the gap between odds ratio and relative risk In our example above, p wine and p no_wine were 0009 and 0012 respectively, so the odds ratio was a good approximation of the relative risk OR = 0752 and RRRelative Risk (RR) is a ratio of probabilities or put another way it is one probability divided by another Odds Ratio (OR) is a ratio or proportion of odds I just remember that odds ratio is a ratio of odds and probability isn't a ratio of odds (AKA it is the other option)
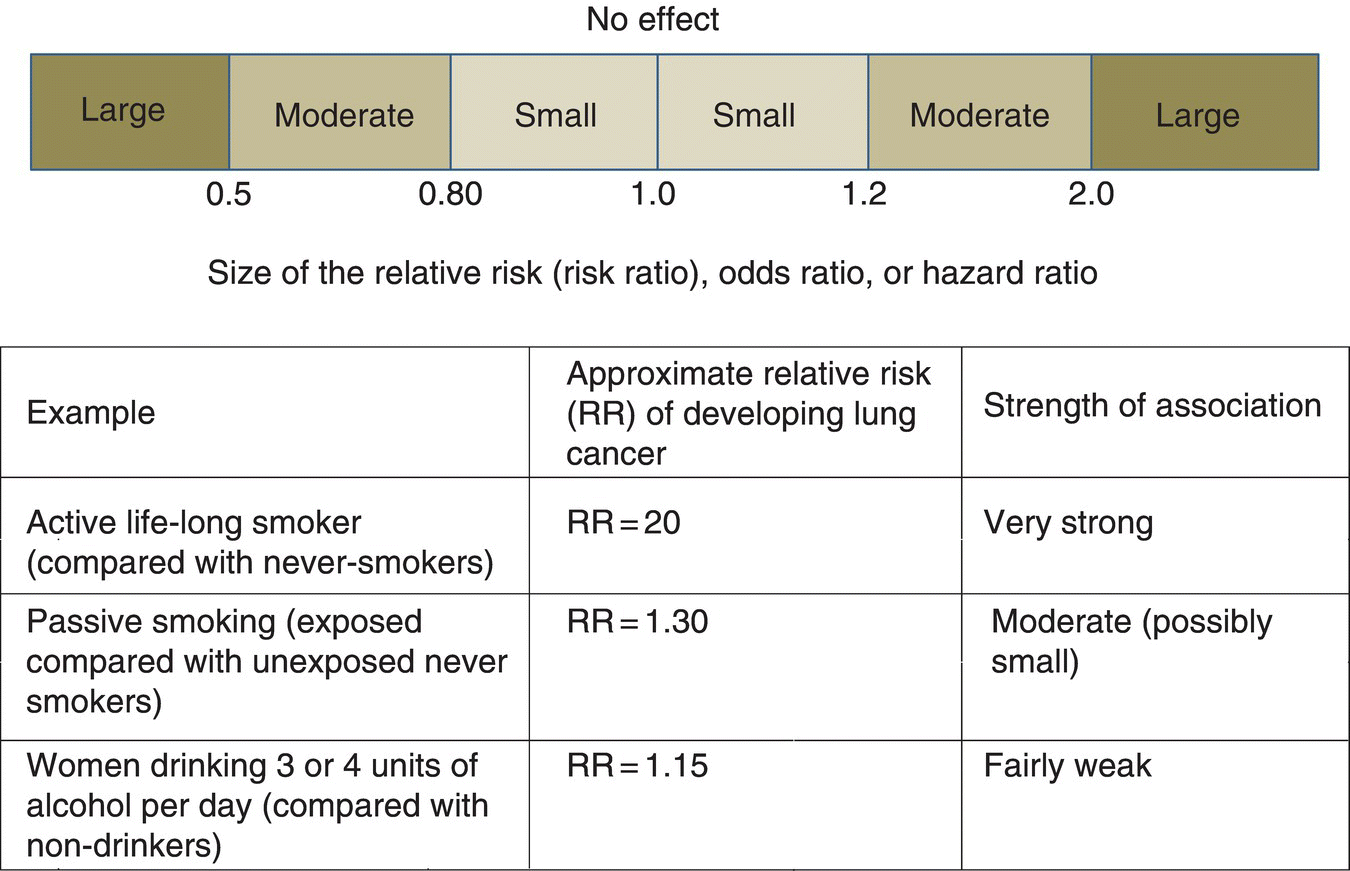
It is assumed that, if the prevalence of the disease is low, then the odds ratio approaches the relative risk Case control studies are relatively inexpensive and less timeconsuming than cohort studies In this case the odds ratio (OR) is equal to 16 and the relative risk (RR) is equal to 865Odds ratios and risk ratios •How do you interpret the relative risk?A value lower than 100 indicates decreased risk The 95% confidence intervals and statistical



Introduction Of Cohort Study Ppt Download



Www Jstor Org Stable
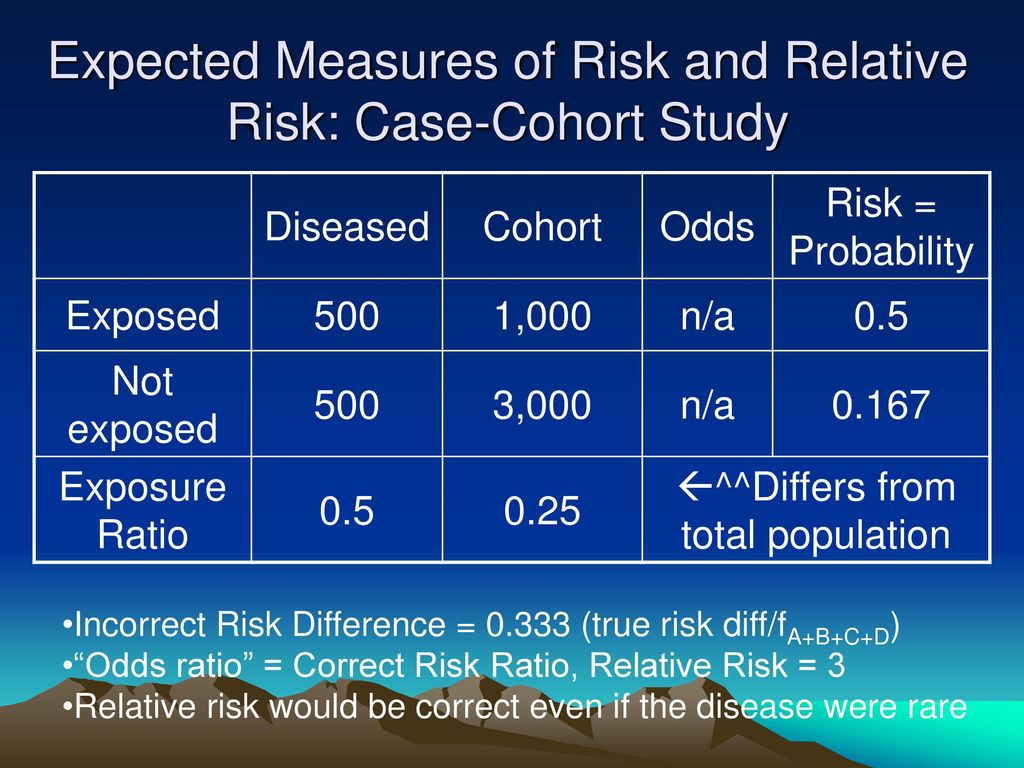
Converting Odds Ratio to Relative Risk in Cohort Studies with Partial Data Information Zhu Wang Connecticut Children's Medical Center Abstract In medical and epidemiological studies, the odds ratio is a commonly applied measure to approximate the relative risk or risk ratio in cohort studies It is well known tha such Even with initial risks as high as 50% and very large reductions in this risk (odds ratios of about 01), the odds ratio is only 50% smaller than the relative risk (01 for the odds ratio compared with a true value for the relative risk of 02) Subsequently, the term relative risk commonly refers to either the risk ratio or the odds ratio However, only under certain conditions does the odds ratio approximate the risk ratio Figure 1 shows that when the incidence of an outcome of interest in the study population is low (




Tablas De Contingencia By Eric Jimenez Issuu




Retrospective Cohort Study Wikipedia
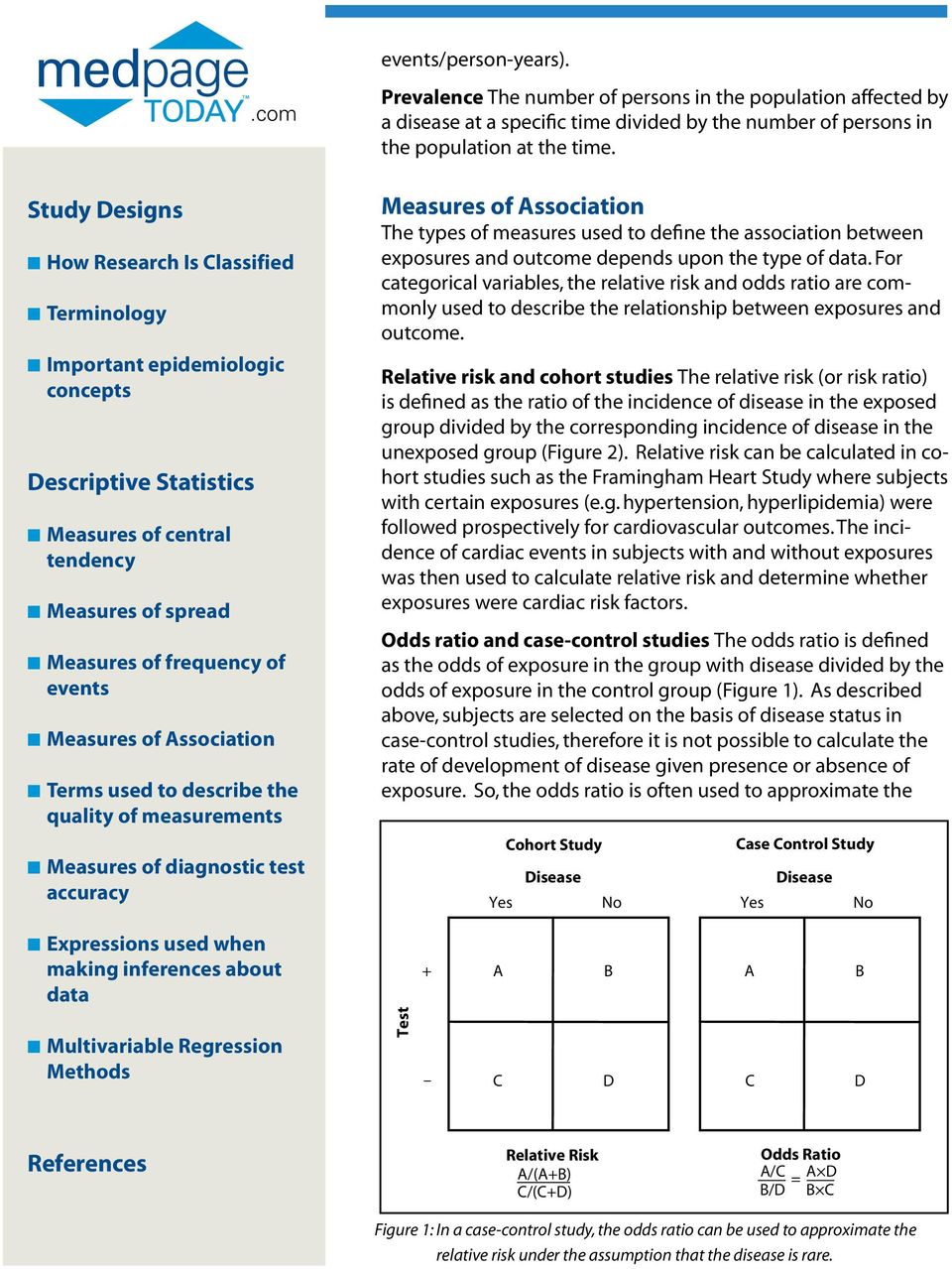
Odds of the disease in men Odds=Risk of disease in men/risk of no disease in men= (140/0)/(60/0)=07 The risk ratio, also referred to as the relative risk, is calculated as the ratio of the risk of the outcome in these two groups In this article, we illustrate, by means of two empirical examples, that use of odds ratios in cohort studies and The measure of association between exposure and disease in cohort studies is the relative risk The relative risk is the ratio of the incidence rate of index subjects to that of control subjects A relative risk of 10 signifies that the incidence rate is the same among exposed and nonexposed subjects and indicates a lack of association between exposure and disease



Epidemiology Knowledge Amboss




Sex Differences In Risk Factors For Myocardial Infarction Cohort Study Of Uk Biobank Participants The Bmj
95%ci ของ rr = 32, 95 2 2 1 1 /2 (1 )100%confidence interval rr log 1 1 1 n p p p z p p Relative risks and odds ratios are widely reported in the medical literature, but can be very difficult to understand We sought to further clarify these important indices Methods We illustrated both relative risks and odds ratios using bar charts, then looked at the types of study for which each statistic is suited The figure on the right depicts odds, the number of patients with the risk factor and the outcome in the numerator and the number of patients with the risk factor without the outcome in the denominator (Odds = 2/8 = 1/4 = 025) RR = relative risk



1




Fully Adjusted Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk For Stroke Compared With Download Scientific Diagram
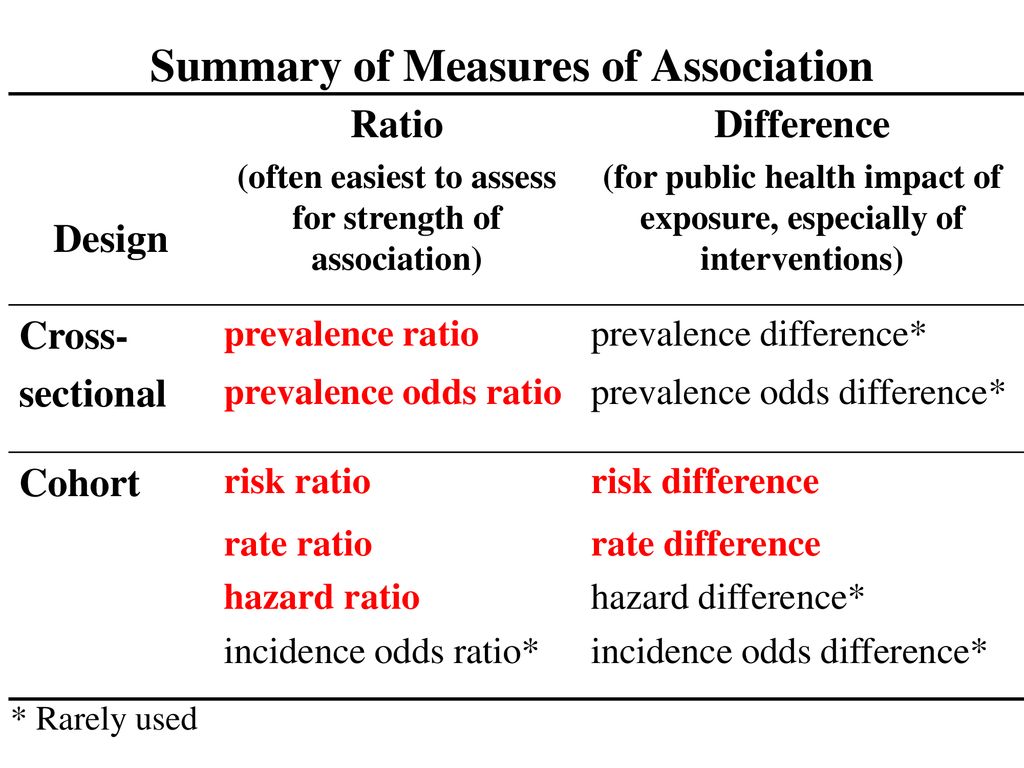
INTRODUCTION Odds ratio (OR) and risk ratio (RR) are two commonly used measures of association reported in research studies In crosssectional studies, the odds ratio is also referred to as the prevalence odds ratio (POR) when prevalent cases are included, and, instead of the RR, the prevalence ratio (PR) is calculatedAs an extreme example of the difference between risk ratio and odds ratio, if action A carries a risk of a negative outcome of 999% while action B has a risk of 990% the relative risk is approximately 1 while the odds ratio between A and B is 10 (1% = If the risk ratio is 1 (or close to 1), it suggests no difference or little difference in risk (incidence in each group is the same) A risk ratio > 1 suggests an increased risk of that outcome in the exposed group A risk ratio < 1 suggests a reduced risk in the exposed group Percent Relative




Risk Factors For Severe Illness And Death In Covid 19 A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Medrxiv



1
The risk ratio is less than 10, indicating a decreased risk or protective effect for the exposed (vaccinated) children The risk ratio of 028 indicates that vaccinated children were only approximately onefourth as likely (28%, actually) to develop varicella as Odds ratio vs relative risk Odds ratios and relative risks are interpreted in much the same way and if and are much less than and then the odds ratio will be almost the same as the relative risk In some sense the relative risk is a more intuitive measure of effect size Note that the choice is only for prospective studies were the distinctionThe relative risk and the odds ratio are measures of association between exposure status and disease outcome in a population Relative risk In epidemiology, relative risk (RR) can give us insights in how much more likely an exposed group is to develop a certain disease in comparison to a nonexposed group Once we know the exposure and disease status of a research population,




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence




Evidence Based Medicine Part 4 An Introduction To Critical Appraisal Of Articles On Harm
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators Risk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three common, but often misused, statistical measures in clinical research In this paper, the authors dissect what each of these terms define, and provide examples from the medical literature to illustrate each of these statistical measures Finally, the correct and incorrect methods to use these measures are summarizedOdds ratio can be calculated in a cohort study and in a casecontrol study − The exposure odds ratio is equal to the disease odds ratio Relative risk can only be calculated in a cohort study 33 When Is Odds Ratio a Good Estimate of Relative Risk?




Effect Sizes Basicmedical Key



Risk And Numbers Needed To Treat Litfl Ccc
Abstract Odds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a risk ratio (RR) Here's the key Relative Risk looks to the future for the effect of a particular cause hence it is used in prospective studies say a cohort study Lets compare the above with Odds Ratio The Odds Ratio can be addressed by asking te following question How many times more likely is a diseased group to have been exposed to a risk factor asIn a control group The odds ratio (OR) is the odds of an event in an experimental group relative to that in a control group An RR or OR of 100 indicates that the risk is comparable in the two groups A value greater than 100 indicates increased risk;



2




Relative Risk Versus Odds Ratio Usmle Biostatistics 4 Youtube
Odds ratio can be calculated in a cohort study and in a casecontrol study The exposure odds ratio is equal to the disease odds ratio Relative risk can only be calculated in a cohort study Odds ratio can be a measure of relative risk in case control study 6 A crude odds ratio can be converted to a crude risk ratio risk ratio = odds ratio/(1 − p0) (p0 × odds ratio), in which p0 is the outcome prevalence (risk) among the unexposed Some have applied this formula to an adjusted odds ratio to obtain an adjusted risk ratio 49 This method can produce biased risk ratios and incorrect confidence Given that this is a cohort study, the relative risk (RR) should have been calculated instead of the odds ratio Odds ratios frequently generate larger differences between exposed and nonexposed groups (especially when dealing with nonrare events), therefore overestimating the observed effect (4)




How To Calculate An Odds Ratio Youtube




Ger1000 Chapter 4 More On Observational Studies Studocu
The odds ratio can also be used to determine whether a particular exposure is a risk factor for a particular outcome, and to compare the magnitude of various risk factors for that outcome OR=1 Exposure does not affect odds of outcome OR>1 Exposure associated with higher odds of outcome ORNonexposed group, "OR" is an odds ratio from a logistic regression equation, and "RR" is an estimated relative risk Most researchers apply this formula to the adjusted odds ratio to estimate an adjusted relative risk Using the formula in this manner is incorrect and will produce a biased estimate when confounding is presentThe term "relative risk (RR)" has been traditionally used to convey the relative probability calculations in both cohort (for incidence ratios) and crosssectional studies (for prevalence ratios




Relative Risk Wikipedia




Questionable Utility Of The Relative Risk In Clinical Research A Call For Change To Practice Journal Of Clinical Epidemiology
Retrospective cohort study Case–control study versus cohort on a timeline "OR" stands for "odds ratio" and "RR" stands for "relative risk" A retrospective cohort study, also called a historic cohort study, is a longitudinal cohort study used in medical and psychological researchWhen used for cohort studies and randomized clinical trials, the odds ratio is often incorrectly interpreted as the risk ratio;Odds ratio = odds of exposure (cases) = ad odds of exposure (controls) bc Cohort studies The relative risk is the measure of association for a cohort study It tells us how much more likely (or less likely) it is for people exposed to a factor to develop a disease compared to people




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




Ppt The Odds Ratio Relative Odds Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6056
The risk of getting the disease in males is 31 times the risk of getting the disease in females •What is the odds ratio for the disease among men as opposed to women? However, one can calculate a risk difference (RD), a risk ratio (RR), or an odds ratio (OR) in cohort studies and randomized clinical trials Consider again the data in the table below from the randomized trial assessing the effectiveness of a newly developed pain reliever as compared to the standard of care9222 Measures of relative effect the risk ratio and odds ratio Measures of relative effect express the outcome in one group relative to that in the other The risk ratio (or relative risk) is the ratio of the risk of an event in the two groups, whereas the odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event (see Box 92a)For both measures a value of 1 indicates that the estimated effects



Http Www Floppybunny Org Robin Web Virtualclassroom Stats Basics Part13 Risks Rates Odds Pdf




Pdf Converting Odds Ratio To Relative Risk In Cohort Studies With Partial Data Information
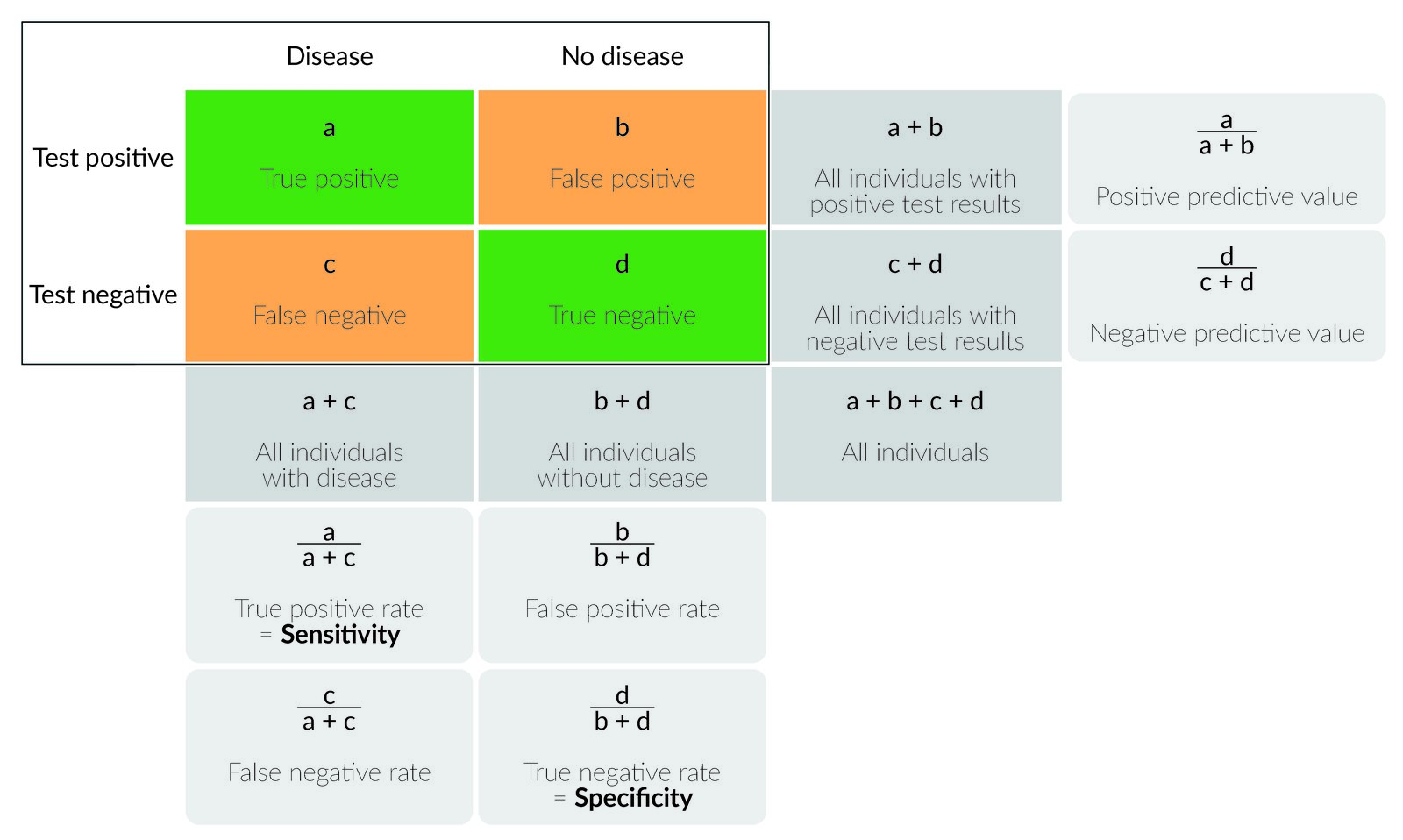
An odds ratio of 112 means the odds of having eaten lettuce were 11 times higher among casepatients than controls Because the odds ratio is greater than 10, lettuce might be a risk factor for illness after the luncheon The magnitude of the odds ratio MantelHaenszel methods for stratified summaries of odds ratios have been extended to summarize risk ratios using matchedpair cohort data (1, 12– 16) The estimator of the risk ratio from the matched pairs reduces to the crude risk ratio described above Using the notation from table 1, this estimator is (A B)/(A C)The odds ratio for lettuce was calculated to be 112 How would you interpret the odds ratio?




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence



Event Based Measures Of Effect Size Asha Journals Academy
Hi, Been reading through a research paper that used a prospective cohort study, but in the results table for measures of association, the odds ratio was used instead of relative riskThe odds ratio then provides an overestimation of the risk ratio, especially when the outcome is frequent The use of logistic regression to adjust for confounding is one of the reasons that odds ratios are presented




Bidirectional Associations Between Covid 19 And Psychiatric Disorder Retrospective Cohort Studies Of 62 354 Covid 19 Cases In The Usa The Lancet Psychiatry




Analytical Studies Note Cohort Study Gives Incidence Relative Risk A R P A R Natural History Of Disease Cohort Study Case Control Study Study



Escholarship Umassmed Edu Cgi Viewcontent Cgi Article 1013 Context Liberia Peer



Www Journalofdairyscience Org Article S0022 0302 12 1 Pdf



Guide To Biostatistics Pdf Free Download



Www Erim Eur Nl Fileadmin Erim Content Images Meta Essentials Meta Analyze Dichotomous Data Pdf




Society For Birth Defects Research And Prevention



Www Teachepi Org Wp Content Uploads Oldte Documents Courses Fundamentals Pai Lecture4 Measures of effect and impact Pdf




Quantification And Interpretation Of Attributable Mortality In Core Clinical Infectious Disease Journals The Lancet Infectious Diseases




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Risk Difference Statistics Tutorial 30 Marinstatslectures Youtube




A Practical Overview Of Case Control Studies In Clinical Practice Chest



1




Measures Of Association Pdf Blood Pressure Odds Ratio




Pdf Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk




Using Odds Ratio In Case Control Studies Youtube



Plos One Bleeding Risk With Long Term Low Dose Aspirin A Systematic Review Of Observational Studies




Epidemiologic Design From A Sampling Perspective Ppt Download




Case Control And Cohort Studies A Brief Overview




Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk



Research Statistics Basics Contents 1 Basic Concepts 2 References Basic Concepts Null Hypothesis The Hypothesis That The Independent Variable Has No Effect On The Dependent Variable For Example Steroids Do Not Improve Outcomes In Ards Would Be




How Can We Convert Rate Ratio To Odds Ratio




Against All Odds Improving The Understanding Of Risk Reporting British Journal Of General Practice




The Following Results Were Obtained In An Chegg Com



Arxiv Org Pdf 1510




Pdf Statistics Review 11 Assessing Risk



Studying Studies Part I Relative Risk Vs Absolute Risk Peter Attia




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Risk Difference Statistics Tutorial 30 Marinstatslectures Youtube



Onlinelibrary Wiley Com Doi Pdf 10 1002 Sim




Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube




Relative And Absolute Risk Video Explanation Osmosis




When Can Odds Ratios Mislead The Bmj




Abdullah Kharbosh What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean By Ebmteacher Casecontrol Cohort T Co Shfiaepl57 عبر Slideshare




Questionable Utility Of The Relative Risk In Clinical Research A Call For Change To Practice Journal Of Clinical Epidemiology




Pdf What S The Relative Risk A Method To Directly Estimate Risk Ratios In Cohort Studies Of Common Outcomes




Ppt Main Points To Be Covered Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Who Saw This In The San Francisco Chronicle In The Past Week Ppt Download




Questionable Utility Of The Relative Risk In Clinical Research A Call For Change To Practice Journal Of Clinical Epidemiology



Www Jstor Org Stable




Ppt Measures Of Association Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




Study Design Comparison Cohort Study Relative Risk




Difference Between Case Control Study And Retrospective Cohort Study



Epidemiologic Design From A Sampling Perspective Ppt Download




Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube



Q Tbn And9gctxz8owky Sul84xtk4ggzacxwhkmhguhlxwyjj9avufagdrhwm Usqp Cau




Risks Of And Risk Factors For Covid 19 Disease In People With Diabetes A Cohort Study Of The Total Population Of Scotland The Lancet Diabetes Endocrinology



2




Critical Numbers Living With Risk Ppt Download



Www Ajicjournal Org Article S0196 6553 17 0 Pdf
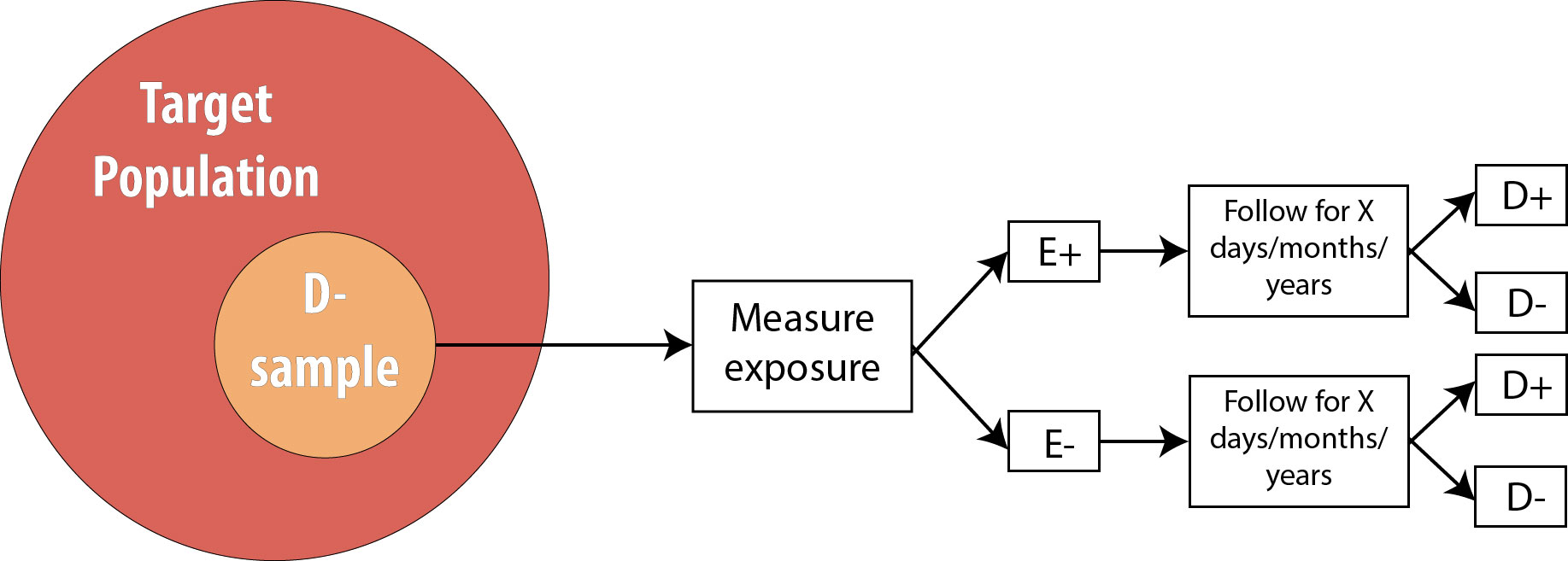



Introduction To 2 X 2 Tables Epidemiologic Study Design And Measures Of Association Foundations Of Epidemiology




Abdullah Kharbosh What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean By Ebmteacher Casecontrol Cohort T Co Shfiaepl57 عبر Slideshare
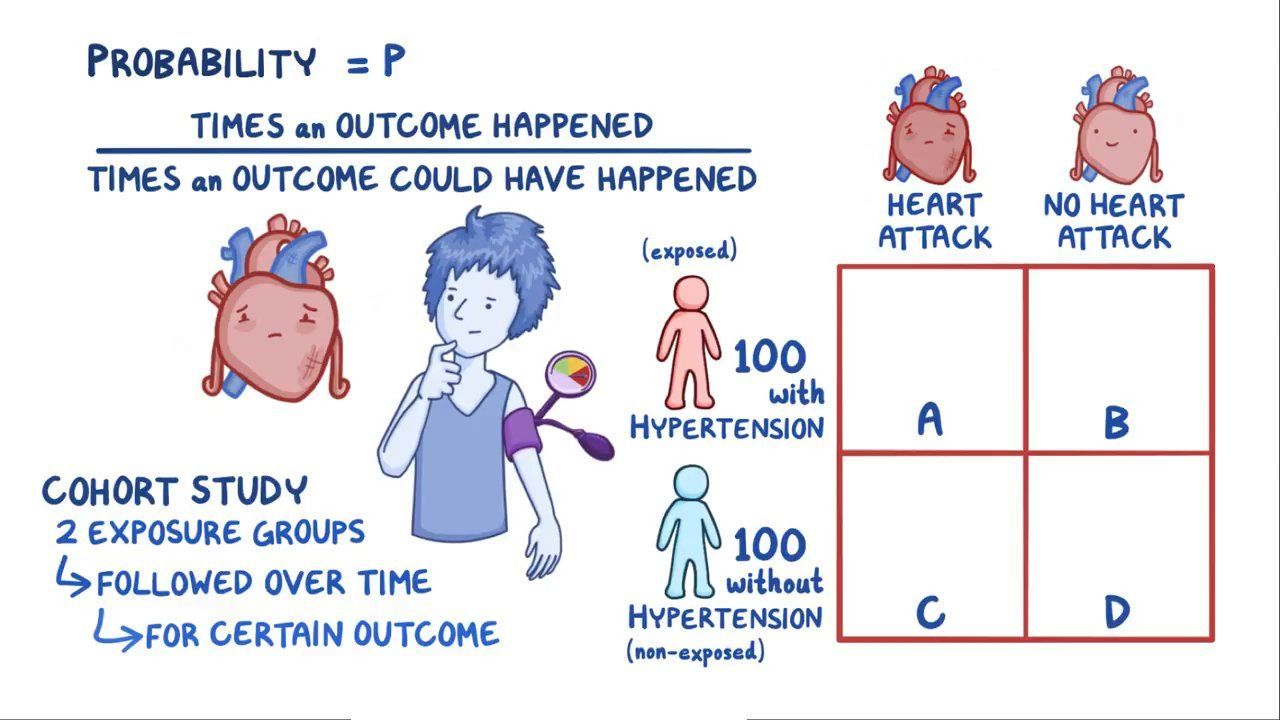



Odds Ratio Video Explanation Osmosis




Estimated Relative Risk Odds Ratio Or Hazard Ratio With 95 Ci For 4 Download Scientific Diagram




How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube




Questionable Utility Of The Relative Risk In Clinical Research A Call For Change To Practice Journal Of Clinical Epidemiology



Case Control Study Vs Cohort Study Pp Made Easy On Vimeo




Fully Adjusted Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk For Hypertension Compared Download Scientific Diagram




How To Calculate Relative Risk 3 Steps With Pictures Wikihow




A Practical Overview Of Case Control Studies In Clinical Practice Chest



Spss Video 10 Obtaining Odds Ratio Relative Risk In Spss Youtube




Measures Of Association Ppt Download




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Calculation Definition Probability Odds Youtube




Ppt The Odds Ratio Relative Odds Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6056




Observational Studies The Ebm Project




Ppt Measures Of Association Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Comparative Validation Of Breast Cancer Risk Prediction Models And Projections For Future Risk Stratification Biorxiv




A Practical Overview Of Case Control Studies In Clinical Practice Chest
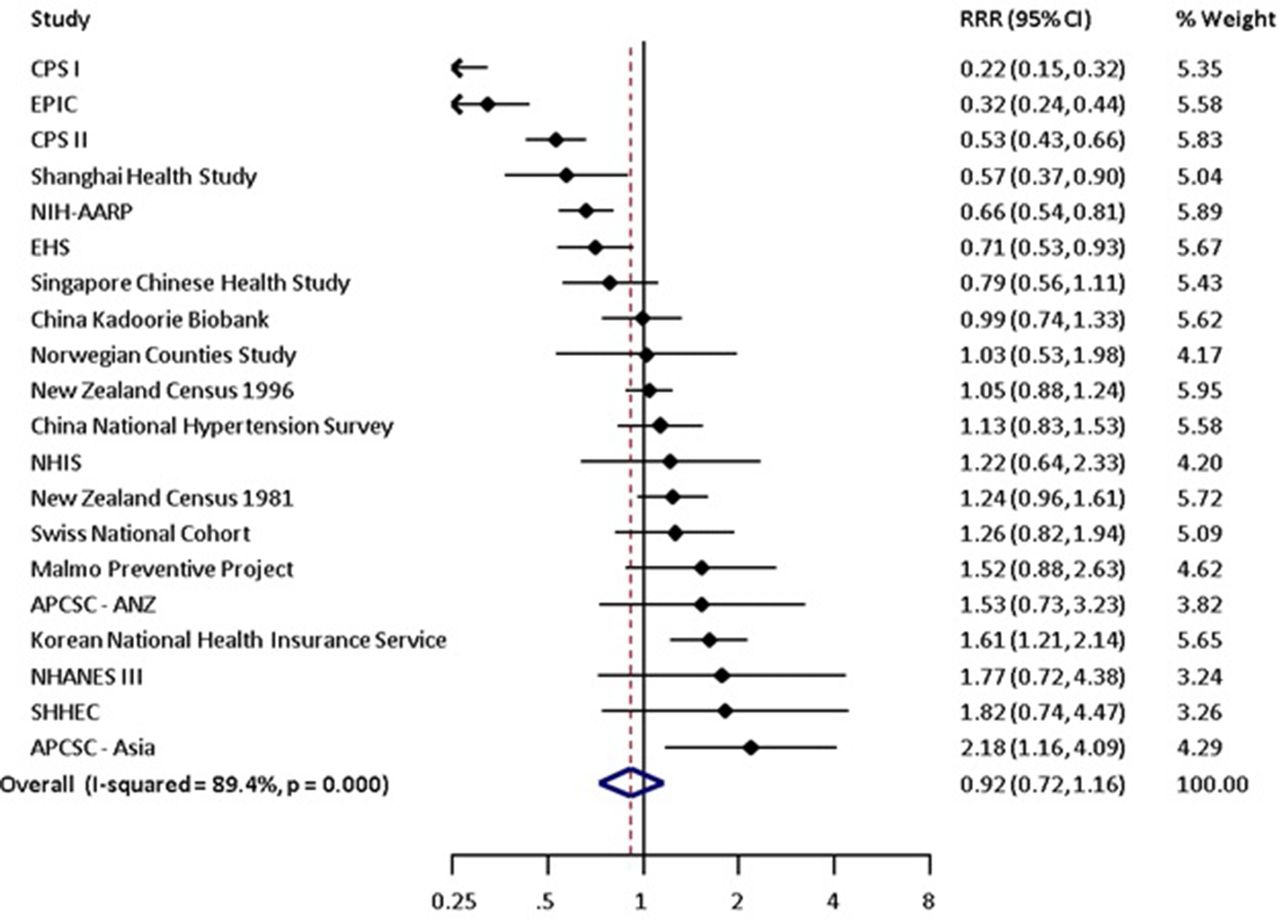



Smoking As A Risk Factor For Lung Cancer In Women And Men A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Bmj Open




Ppt Main Points To Be Covered Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Questionable Utility Of The Relative Risk In Clinical Research A Call For Change To Practice Journal Of Clinical Epidemiology




Using Bayes Nomogram To Help Interpret Odds Ratios Bmj Evidence Based Medicine




Figure 1 From Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors Ssris And The Risk Of Congenital Heart Defects A Meta Analysis Of Prospective Cohort Studies Semantic Scholar




Effect Sizes Basicmedical Key




What S The Relative Risk Odds Ratio Applied Mathematics



Www Jstor Org Stable




Werkgroep Uitwerkingen Farmacoepidemiologie Werkgroep 1 Opdracht 1 En 2 Studeersnel




Relative Risk And Odds Ratio R Erol Sezer Ppt Download



Epidemiology Knowledge Amboss


